IBM Talent Assist
A video interview application designed to assist recruiters analyze prospective job candidates.
Overview
As a part of my capstone project, I worked with IBM to design a Video Interviewing Application to improve the process of talent acquisition.
IBM was looking to innovate within the field of recruiting and my team received an open challenge to create a solution that would improve the existing process. The project involved an exploratory study which led to the design of a Watson Assisted Interviewing Application for better information elicitation during candidate interviews.
My team – Sandeep Jagtap (Project Manager), Arvind Santhanam (UX Researcher), Me (UX Designer)
Activities performed – Literature Review, Interviews, Synthesis, Sketching, Wire-framing, Concept Validation, Visual Design, Usability Testing.
Timeline – 6 months
Project Objectives
1. Study and understand the field of Talent Acquisition
2. Identify opportunities for improvement
3. Design a solution to improve the existing process
Process

Exploratory Research
To kick off our project, we had stakeholder interviews to understand IBM’s expectations, and an exploratory study was designed to help us better understand the process of recruiting. Our study was designed to understand both recruiters and job seekers because we believed that an improvement to help either stakeholder could result in an improvement in the overall process.
The research questions were:
1. What is the existing process followed by recruiter and job seeker?
2. What are the different roles involved?
3. What are the tools used to support these roles?
4. What are some of the opportunities for improvement?
1. Literature Review
Since we did not know much about recruiting, data from multiple sources was gathered for our preliminary research. The information helped us understand the research gaps that needed to be clarified and the assumptions that needed to be validated.
1. Our sources included academic papers, industry articles, reports, and white papers to understand the existing scenario of talent acquisition.
2. The information we gathered was organized into the subject categories below to understand the broad themes that we were interested in.
Categories from Information Mapping
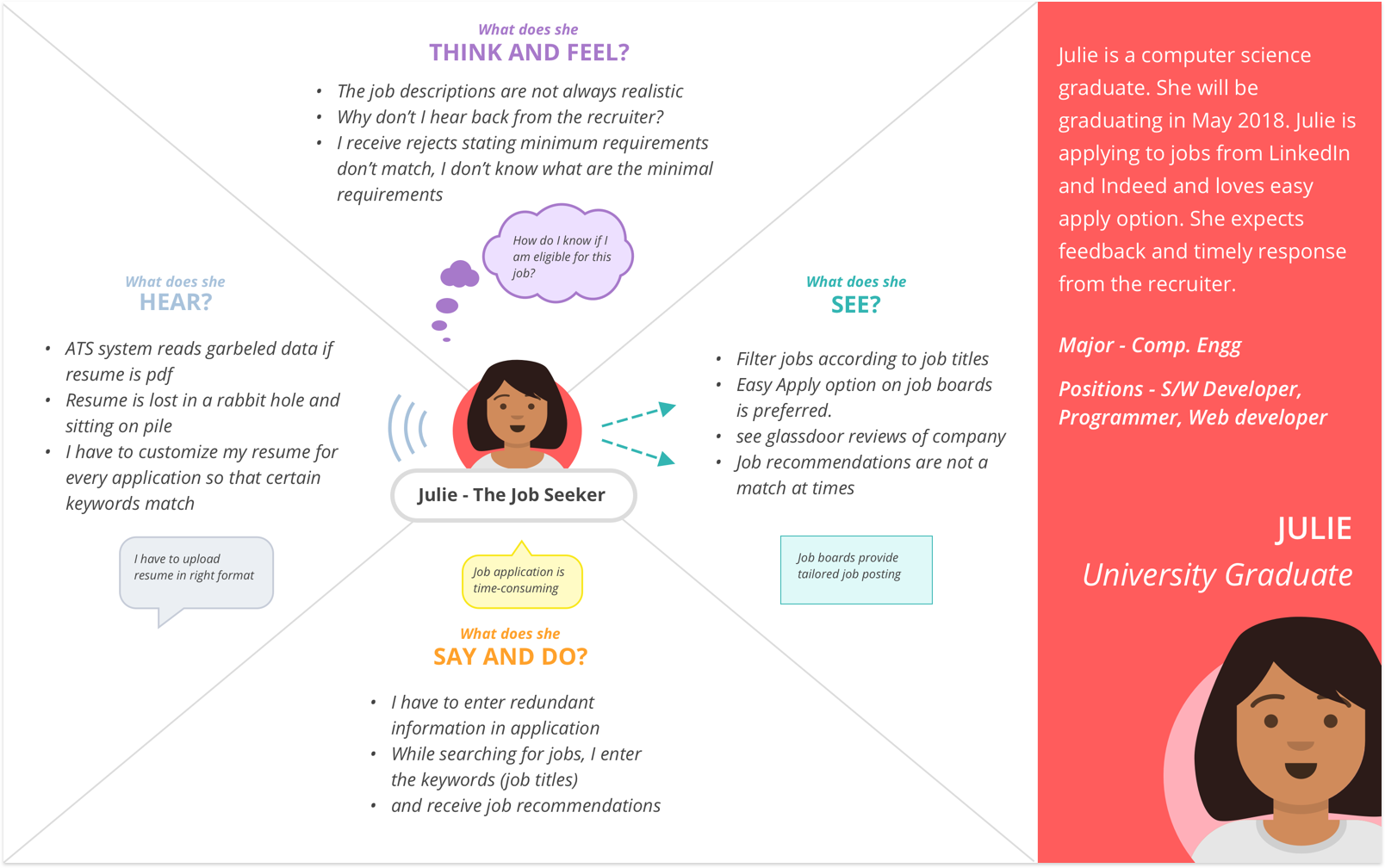
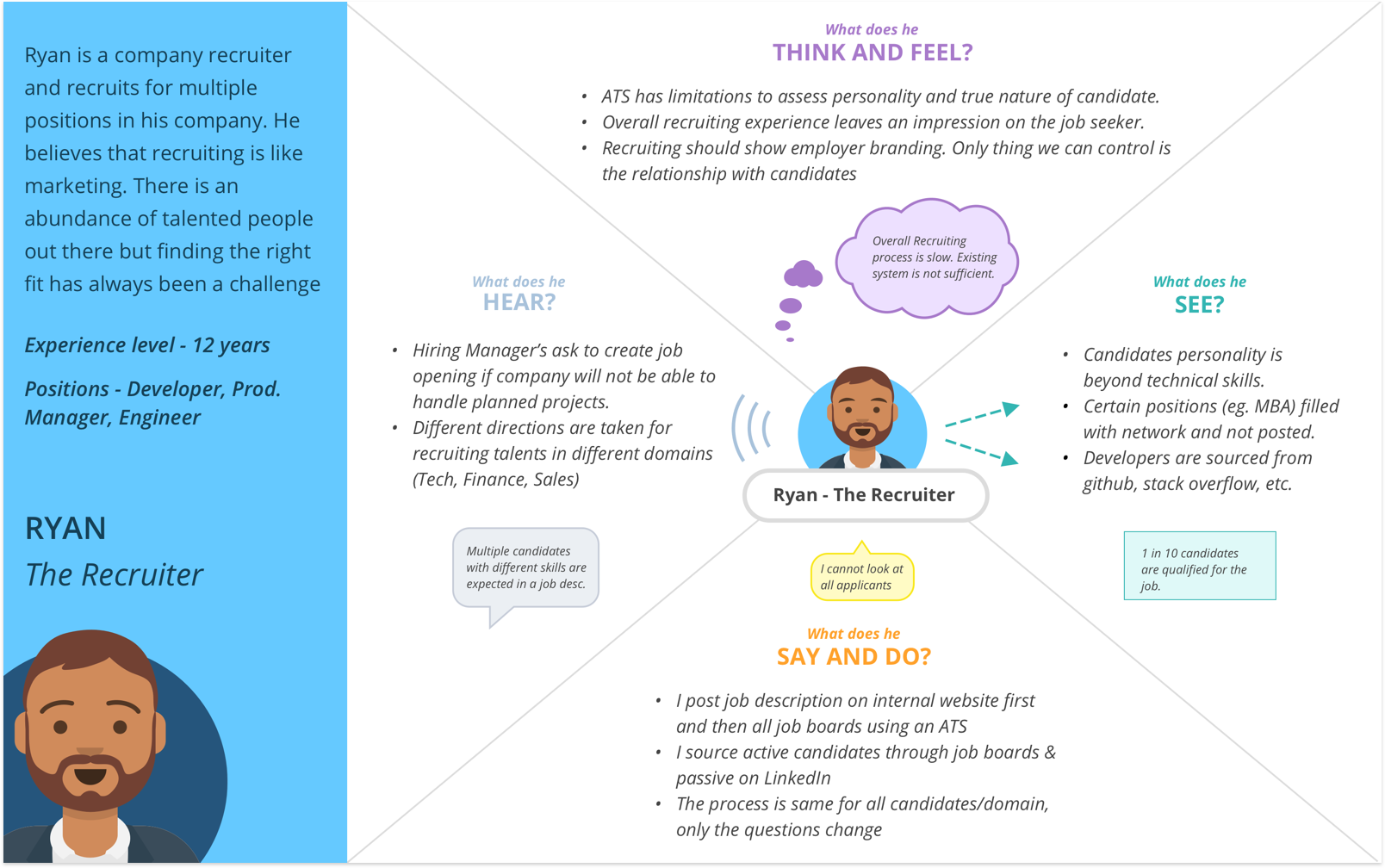
2. Participant Interviews
With the gathered information, we interviewed participants to help us better understand the field and validate our understanding. Participants shared information and mentioned what they would like to have changed, and a majority agreed that there was scope for improvement in their work.
The following steps were used:
1. Interview protocols were created for both recruiters and job seekers.
2. Recruited participants through social media applications such as LinkedIn, Slack, Facebook etc.
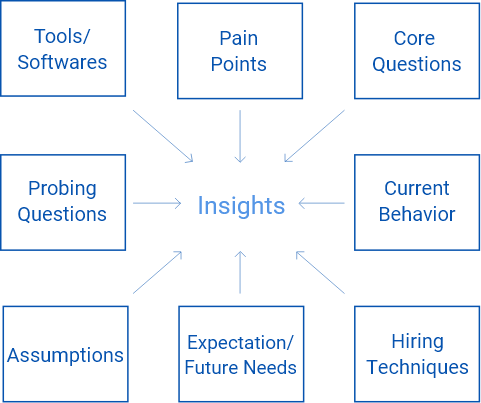
3. Conducted 11 out of 24 in-depth interviews; 30 – 60 minutes each.
4. Summarized interviews and shared information through Google Docs.
Diversity of Participants for Interview
3. Technology Review
The gap between recruiting different participants was used to review some of the popular recruiting tools mentioned by our participants. Some of the tools were studied at a high level due to limited public access and we realized that there was a push towards using AI-based systems, connected services, and automated interview technology to minimize the role of the recruiter.
The following steps were taken:
1. Recruiting tools were analyzed for their innovative features and unique selling points (USP).
2. Miscellaneous tools studied for alternate inspirations.
3. Contextual inquiry sessions were conducted to understand how recruiters use ATS software to track and organize their recruiting.

Tools Studied in Review
Synthesis and Insights
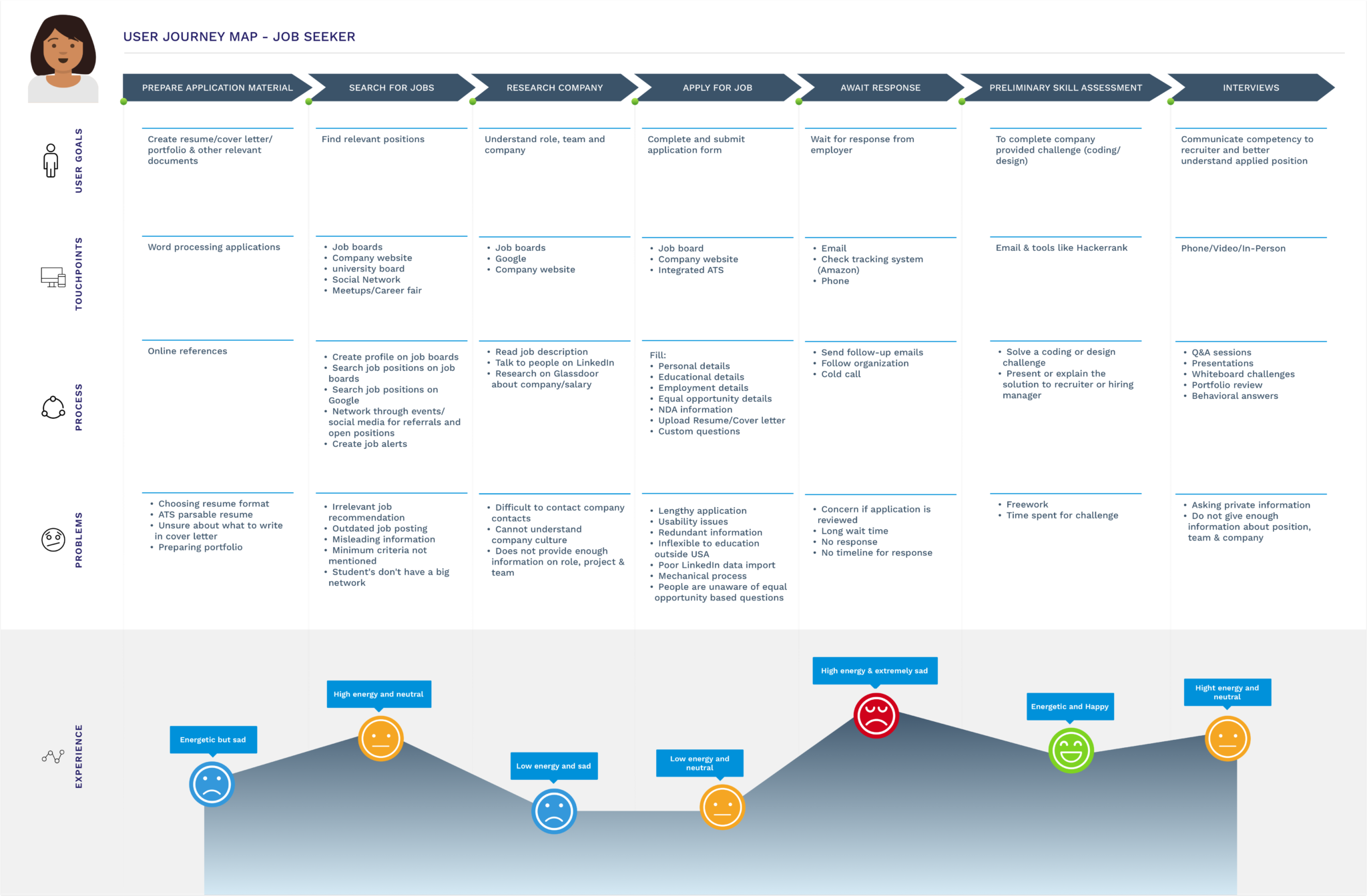
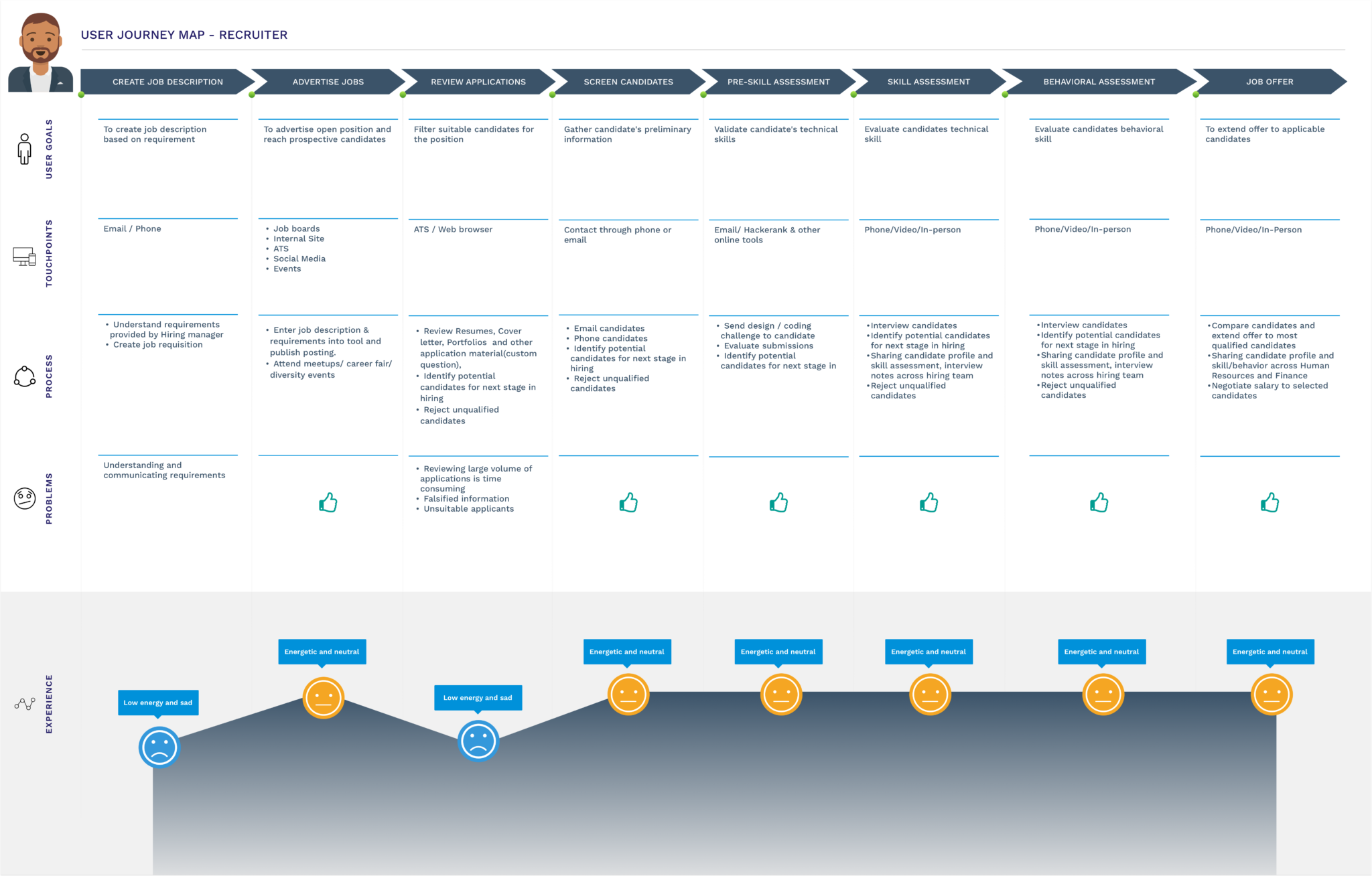
The interview summaries were coded to create an empathy map and journey map to externalize our insights and better understand the roles.
Some of the quotes that stood out were:
1. ‘ATS and tools only help me organize the process, I still have a lot of work to do in finding the right candidate’ – Recruiter
2. ‘Staffing agencies can be really accurate at finding good candidates for a role… they tend to know the candidates well enough to understand who we’d be interested in.’– Recruiter
3. ‘Culture fit is really important. It’s easy for me to train or teach someone something, but their basic personality is something that we don’t have any control over.’ – Recruiter
4. ‘Companies often have unrealistic job expectations… it’s difficult for me to decide whether the company is a good fit for me or not‘ – Job Seeker
5. ‘Applications can be time-consuming to fill… It’s just easier to use job boards sometimes. They have a ‘one-click’ function… that’s easier.’ – Job Seeker
Challenges
1. Difficulty contacting and recruiting target participants. Participants from IBM were recruited for specialized roles that were difficult to set up.
2. Heavy improvisation in conducting interviews involved frequent follow-up clarifications to reach significant depth in information.
3. The limited public access to recruiting tools was compensated by high-level analysis of multiple products than our initial plan.
4. Interviews gave us a lot of qualitative information and it was difficult to code the data and find thematic maps.
5. The coded information needed to be collectively understood to create an empathy and journey map that best fitted the narrative of all participants.
Research Outcome
1. The above methods helped us gather enough information to fill research gaps and answer the research questions we prepared initially.
2. Next steps were to scope the problem, identify opportunities, and design a solution.
Problem Focus
Since there was no investment expected from the job seeker, and since he played a very reactive role, we decided that the recruiters would be the primary stakeholders for the solution. With problems to solve at different stages in recruiting, we wanted to focus our efforts on one only problem that would create the best benefit. We organized ‘likes’, ‘wants’, and ‘frustrations’ and created a category map to help us think about different solutions that we could possibly work on.
Some of the ideas for both recruits are job seekers were:
1. A set of quizzes that are experience based to help filter an initial set of applicants.
2. Time-based challenges through a Content Management System(CMS) to help filter candidates.
3. An Application Tracking System (ATS) for job seekers to receive recommendations and manage their applications.
4. Using AI, or conversational interface to assist filtering and talent matching.
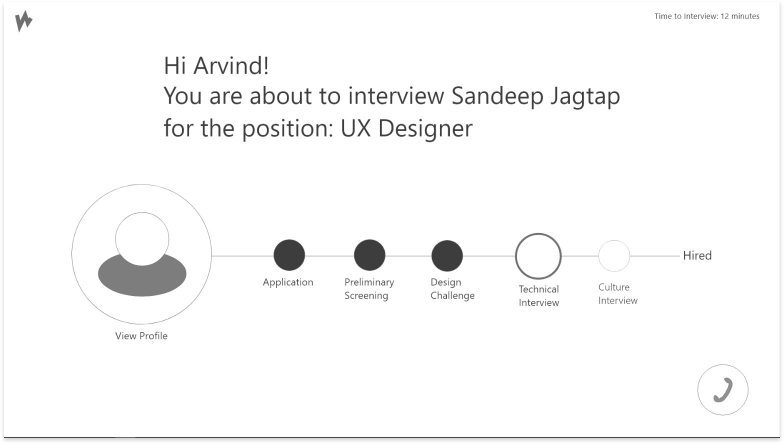
Through discussion, we came to realize that conversation played an important role in helping recruiters understand their candidates. We knew from our technology review that AI assisted software was becoming more prevalent. So, we decided to explore the idea of a Watson assisted interviewing application to facilitate conversation, and help recruiters better filter job candidates.
Concept Design & Validation
To create an interviewing application to help recruiters, we needed more contextual information to help us design the solution. A ‘Participatory Design/ Evaluation’ was used to iterative gather information, design a prototype and later evaluate it.
We were interested in answering the following questions to help us design the solution:
1. How do recruiters prepare, conduct and review interviews?
2. What information/ functions can we provide to help ease their effort?
Concepting
The goal – We wanted to validate our idea and see if people would like to see us build our solution.
1. Application mockups were designed to help visualize our idea.
2. Participants were interviewed (semi-structured) to understand how they felt about the application and their inputs.
Low-Fidelity Exploration
The goal – We wanted more clarity on how recruiters / hiring managers conduct interviews and the functions that they would find useful through our application.
1. Sketches and lo-fidelity mockups were created to explore ideas.
2. I interviewed participants (semi-structured) on a hypothetical scenario and how they would approach a set of tasks for them to complete. Later, I showed them our lo-fidelity mockups to compare what they said to the ideas that we had come up with.
Mid-Fidelity Exploration
The goal – We wanted to think about layout, information organization and validate functions present in our application.
1. Iterative mid-fi mockups were designed that improved with every interview.
2. I interviewed participants by creating a scenario and walking them through how I would use the solution. I asked the participants for their input at every stage to see if what our ideas made sense, and if there was anything that they would like to change/ improve.
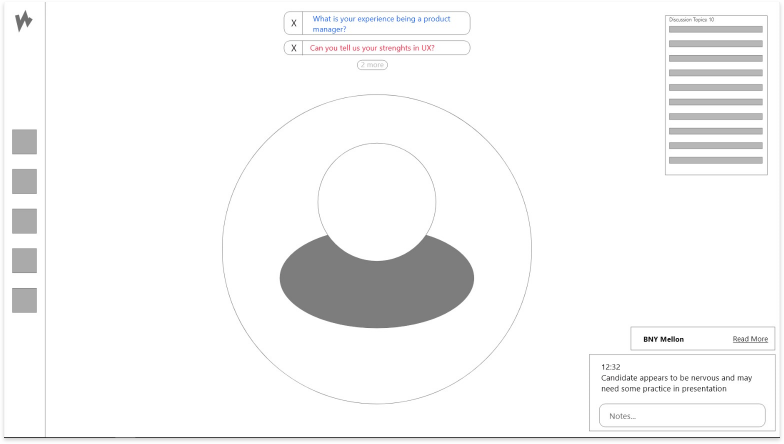
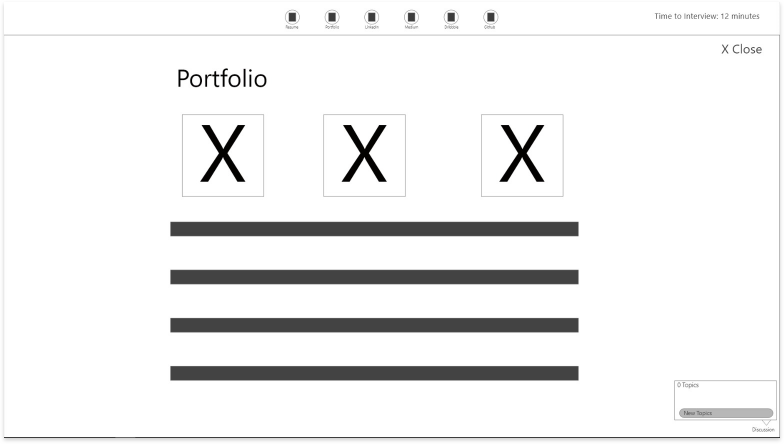
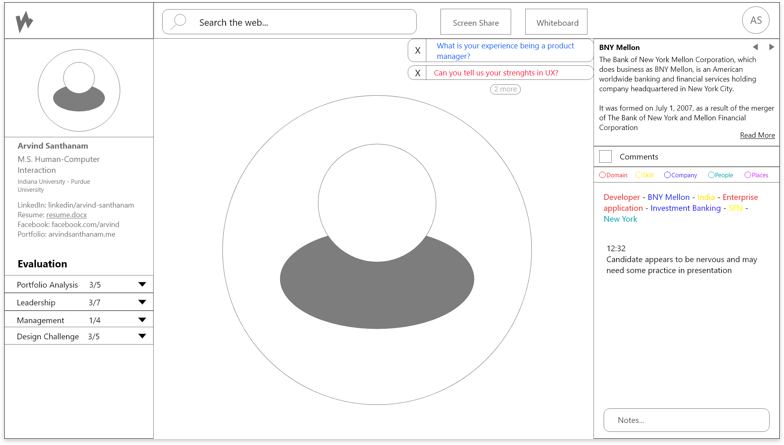
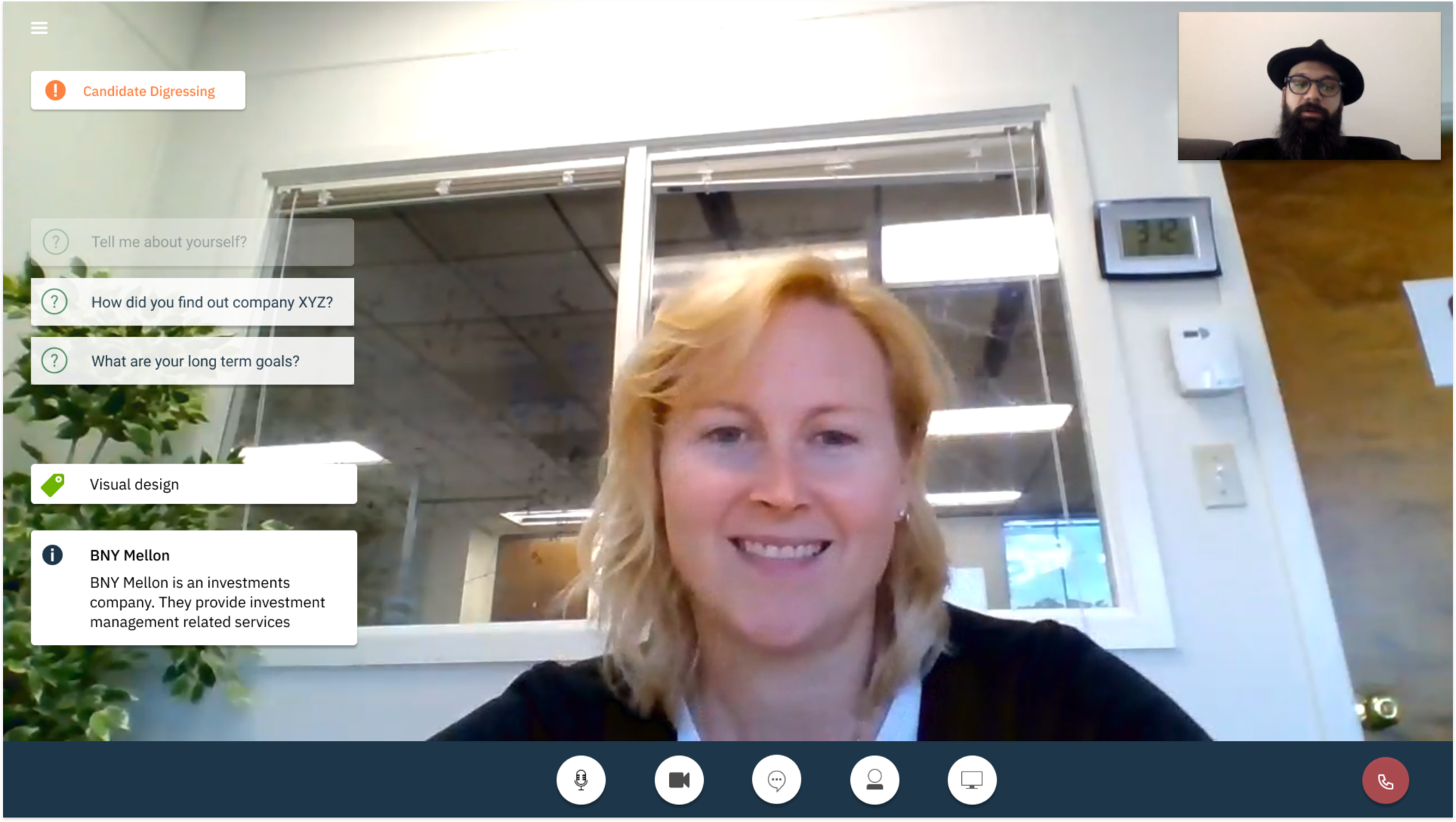
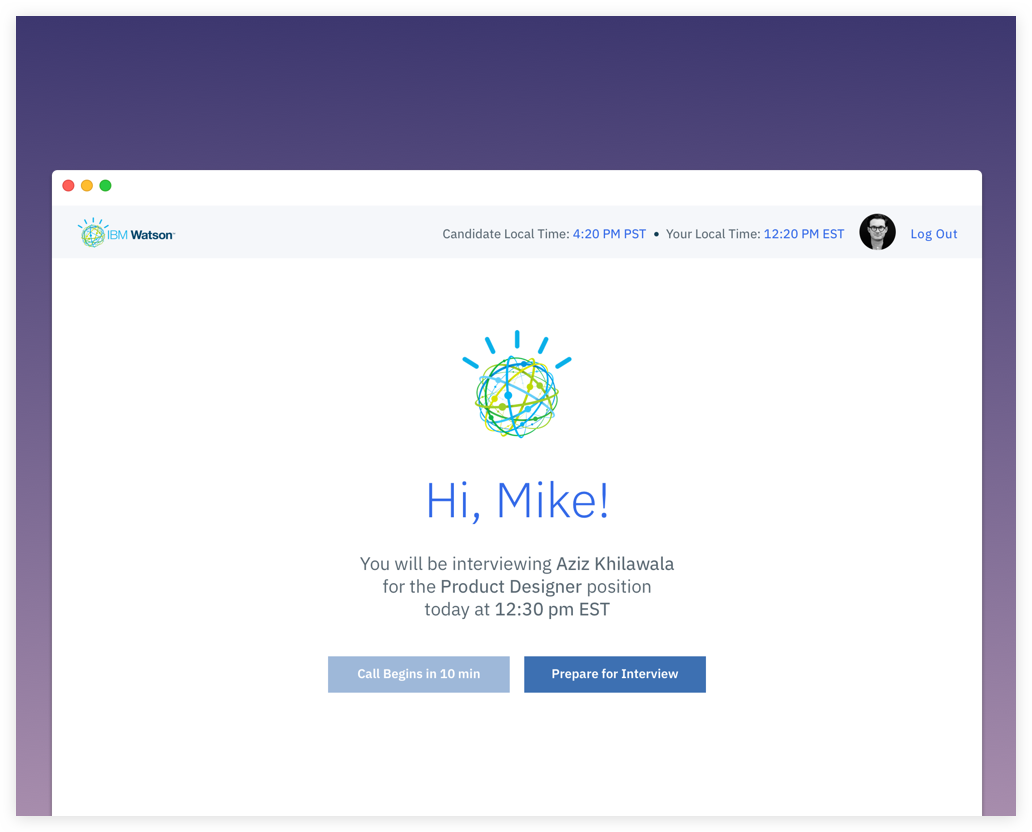
High-Fidelity Exploration
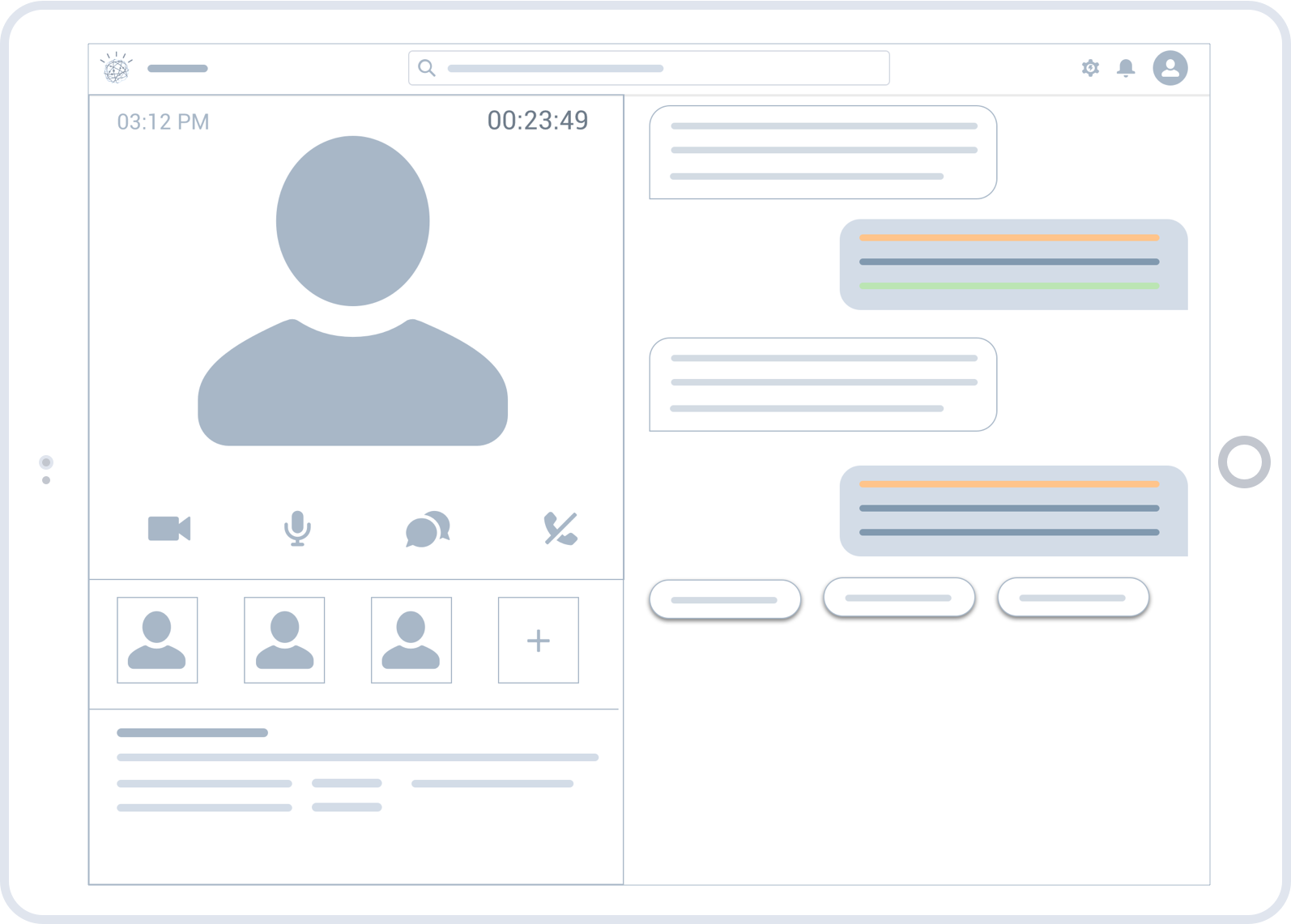
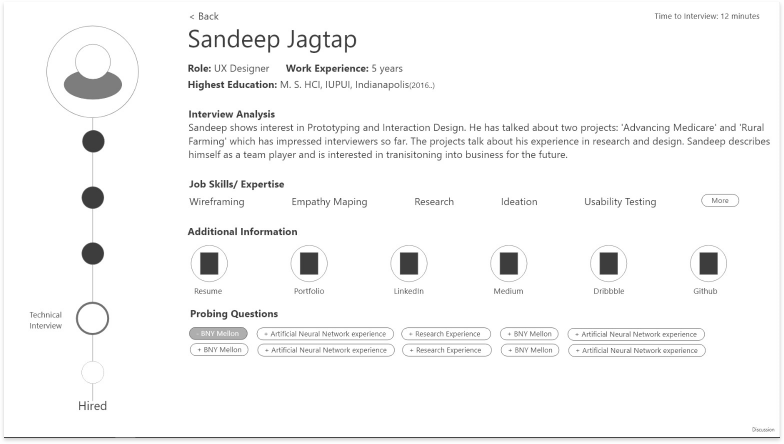
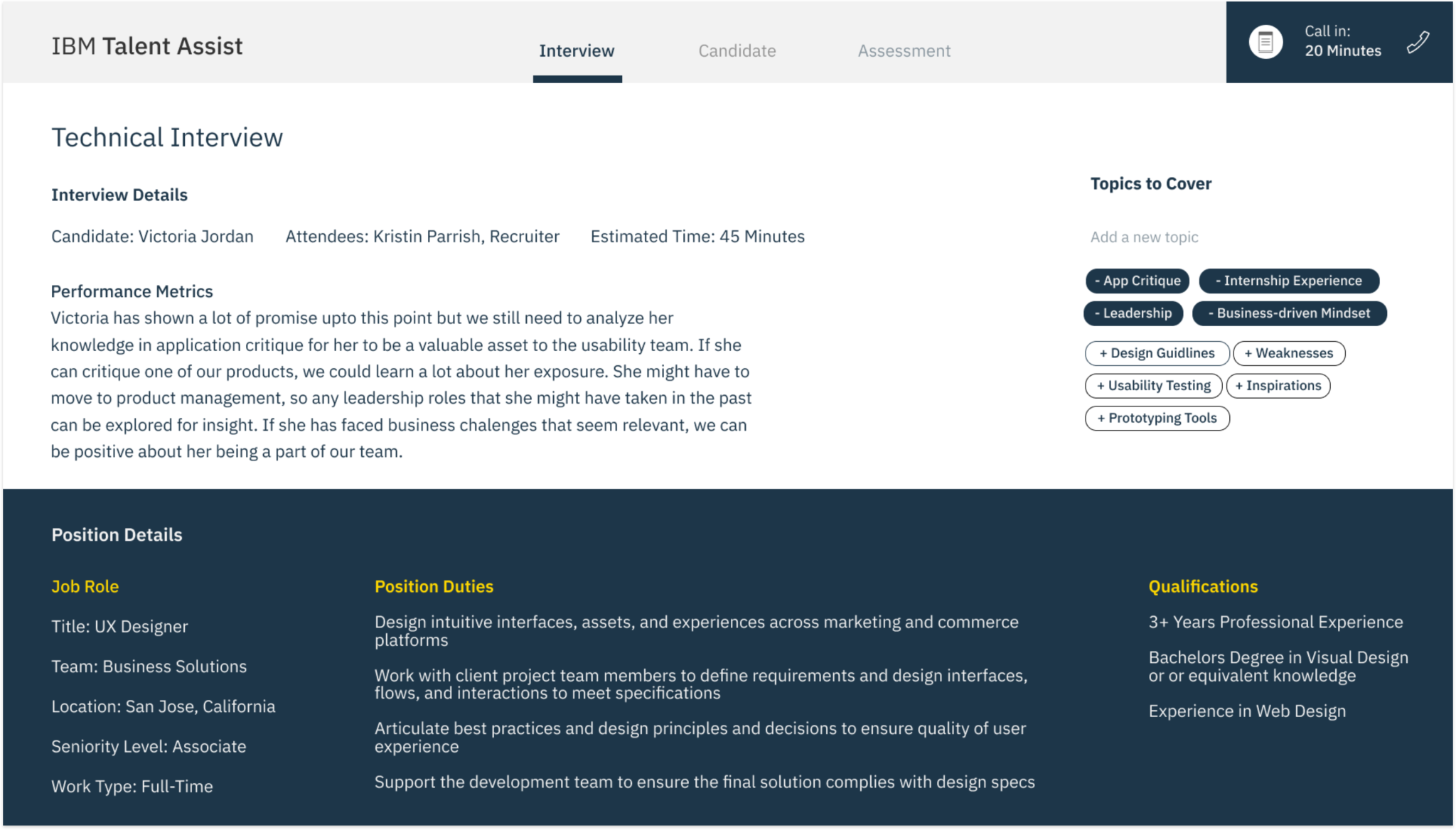
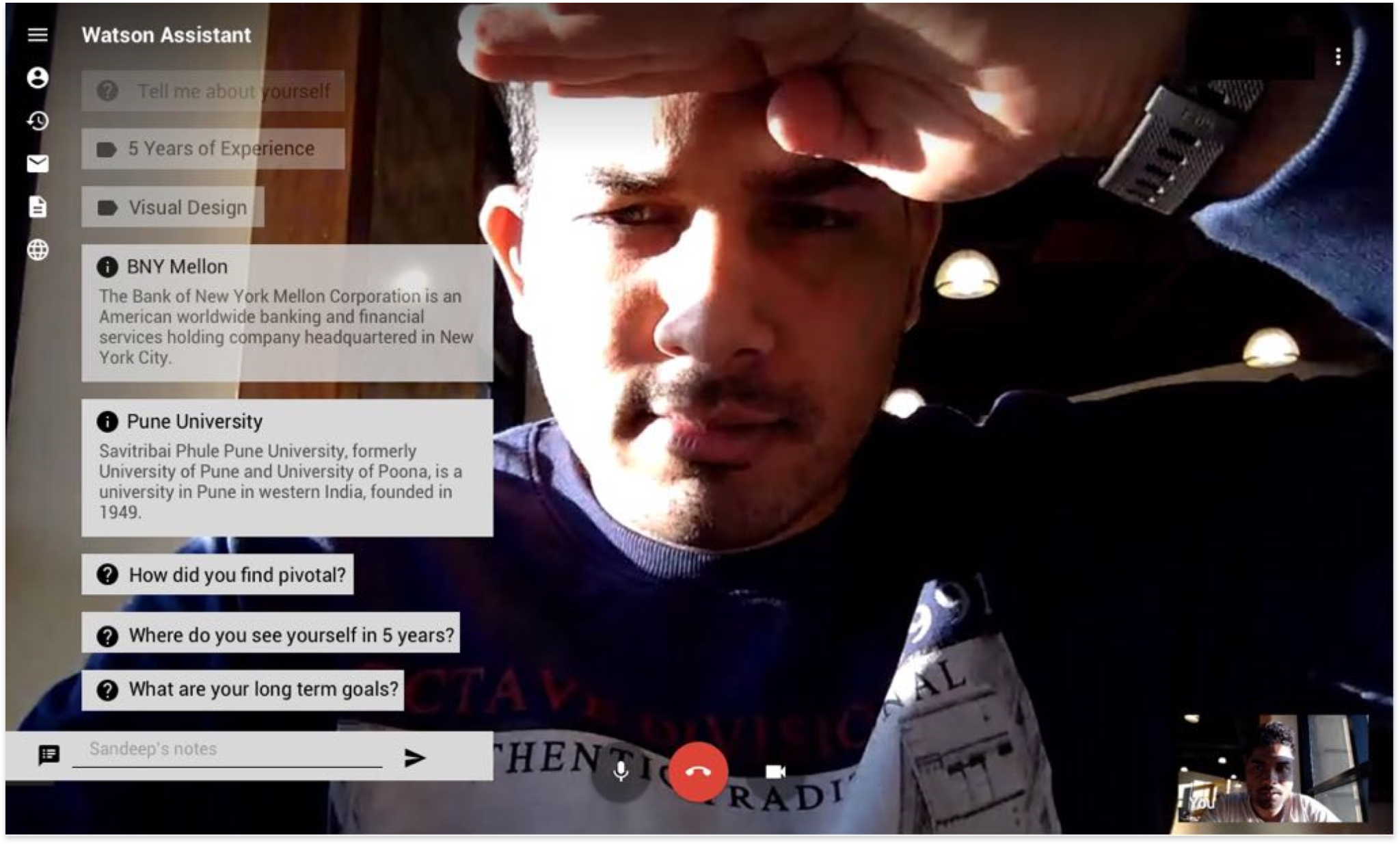
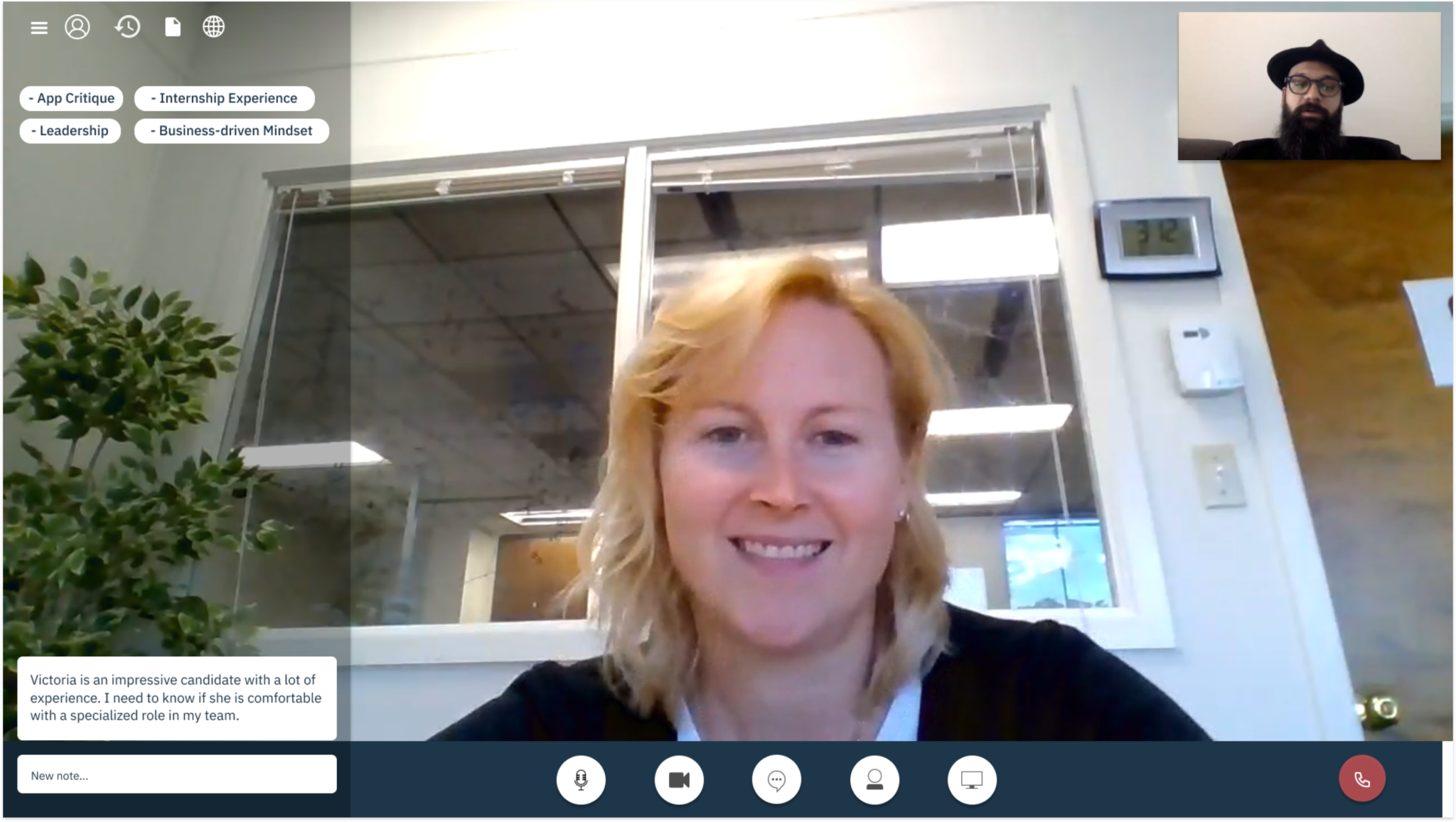
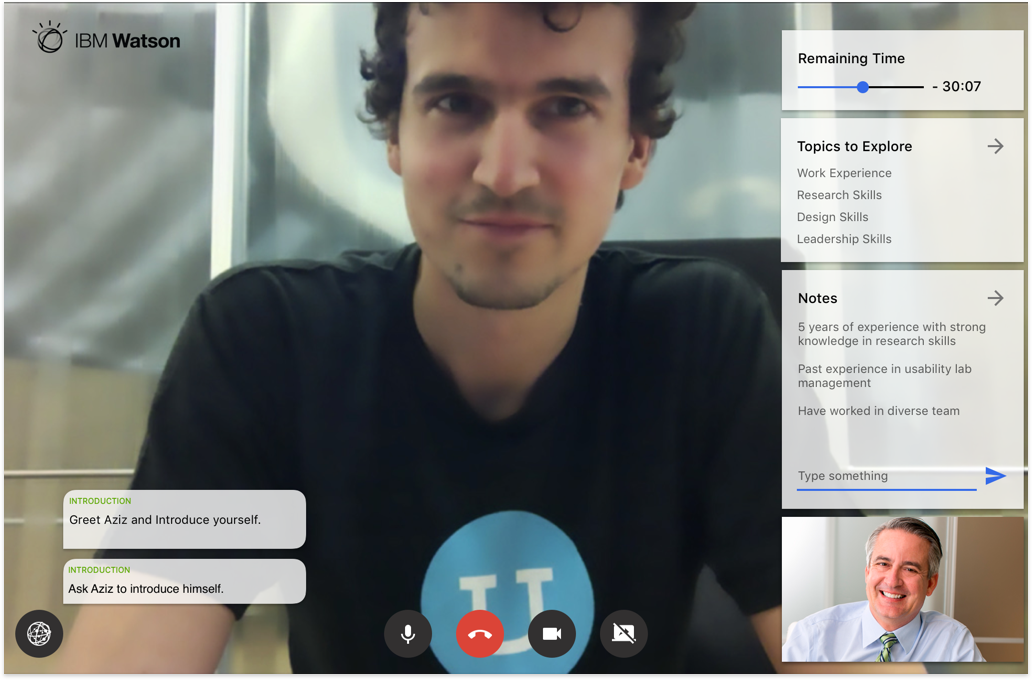
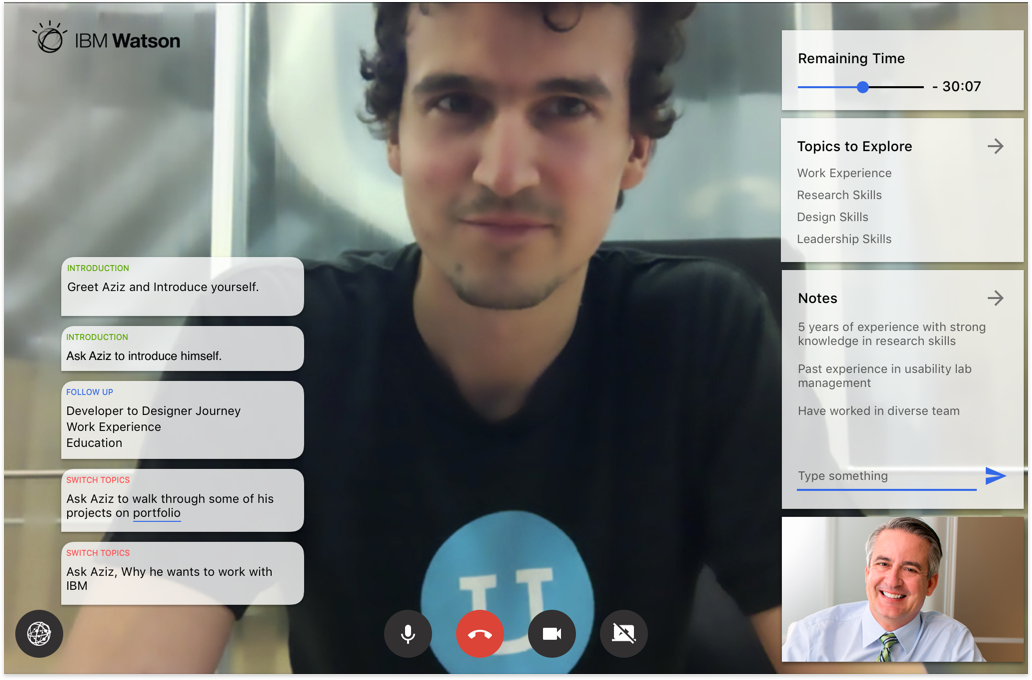
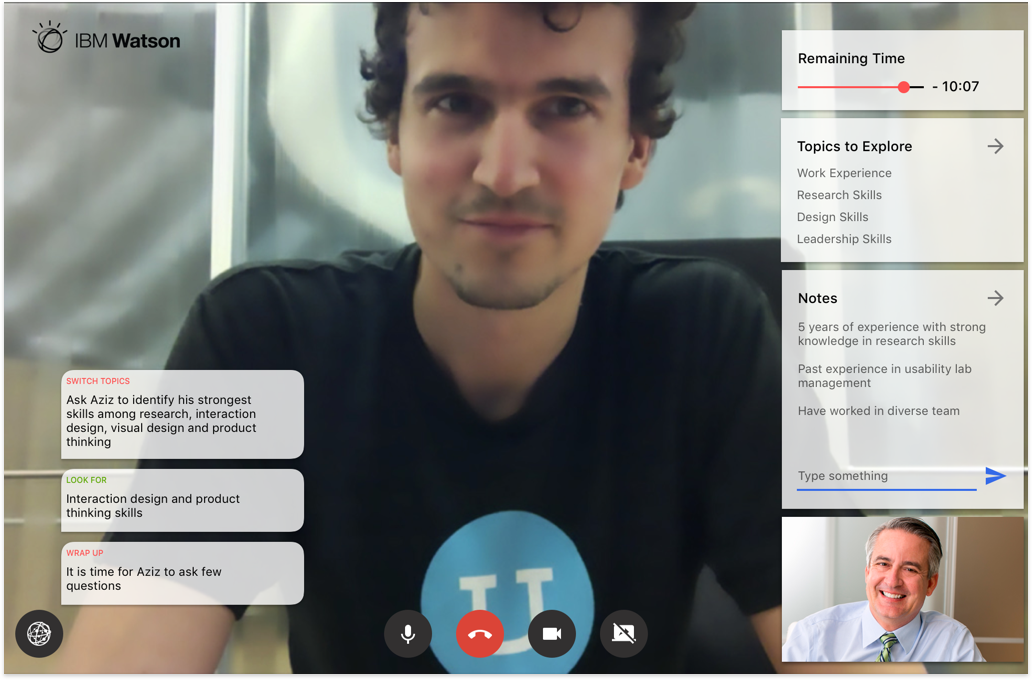
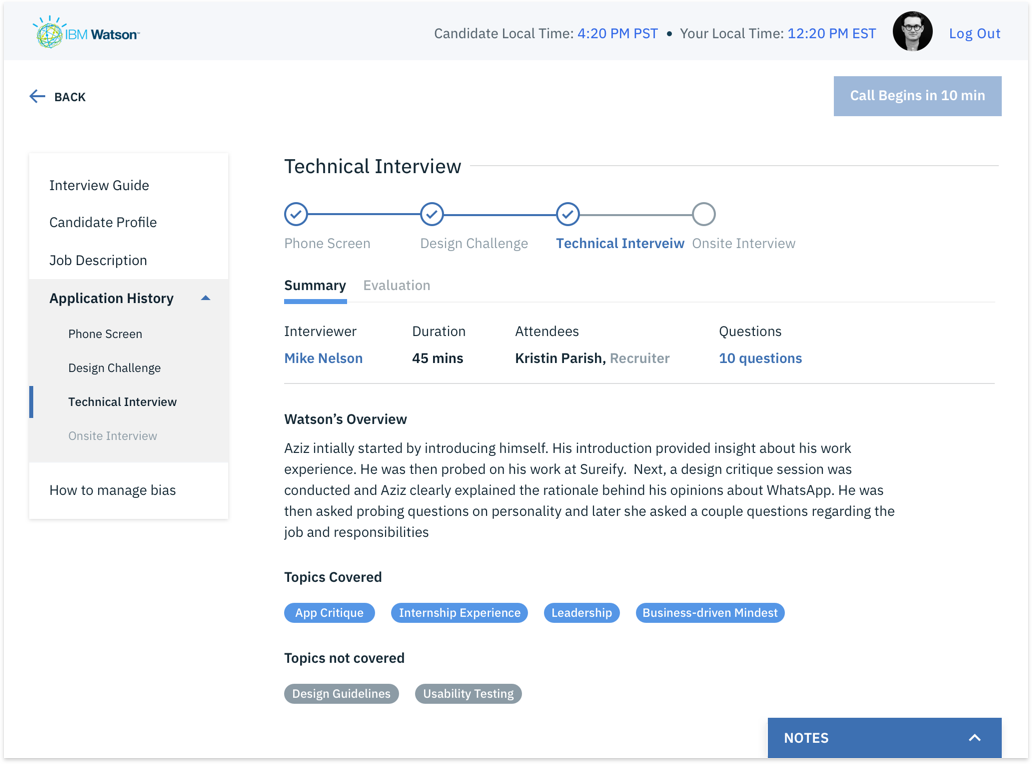
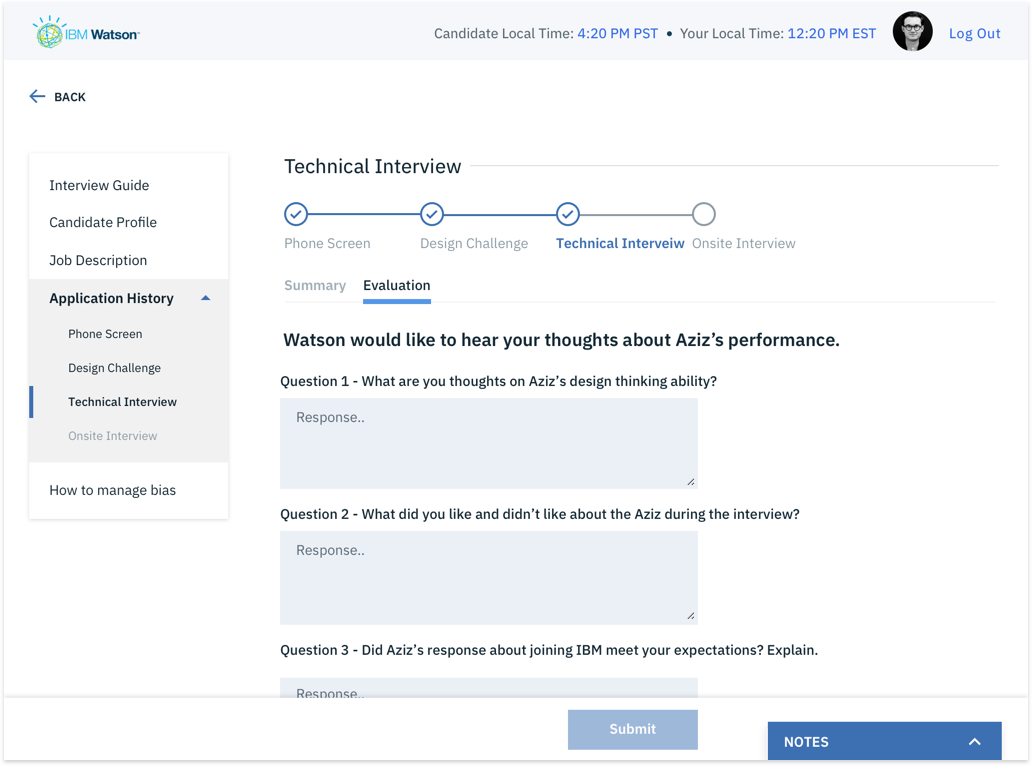
The goal – We built an end-to-end solution that needed to be tested for usability issues and design improvements.
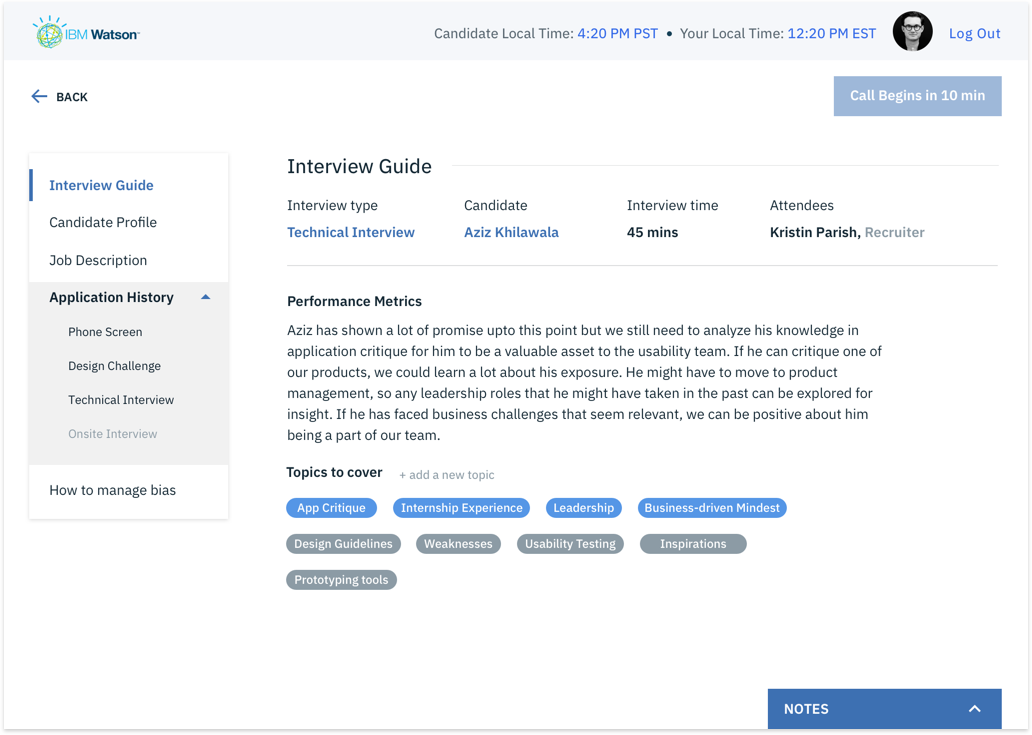
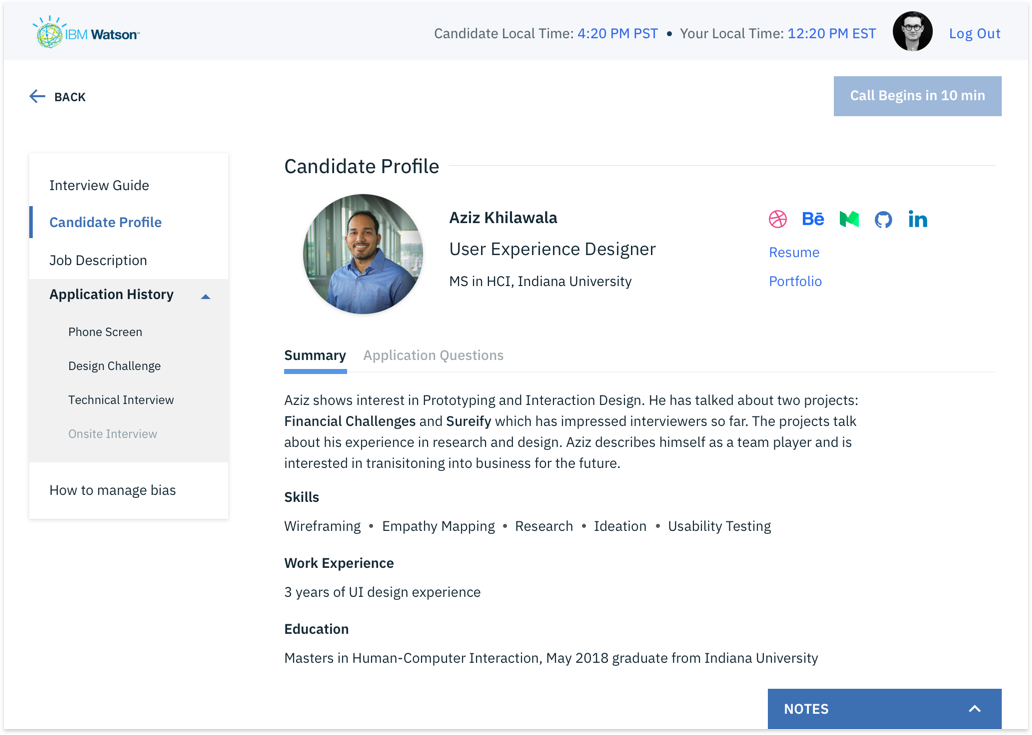
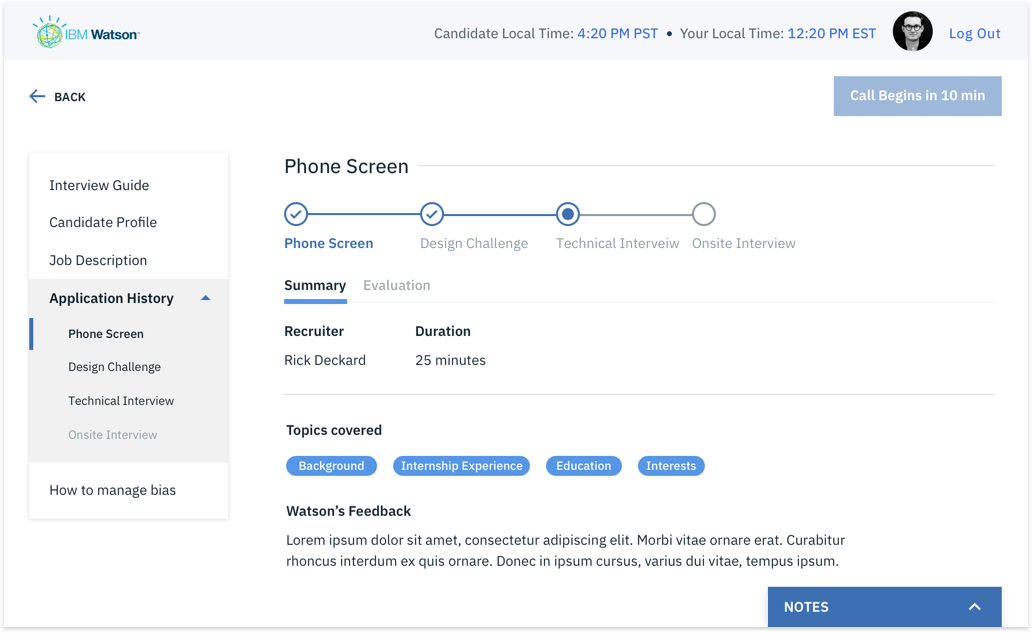
1. Complete Hi-fi designs were created for Hiring Managers based on the collective insights gathered from previous interviews.
2. I conducted remote usability evaluations through screen sharing. Participants were given a real-world scenario and a set of tasks to complete. Both quantitative and qualitative information was gathered. Observations were made by a note-taker. A detailed summary of evaluation can be seen in this evaluation protocol.
Conclusion & Future Work
Based on the suggestions and feedback from the candidates, we were able to understand areas for additional exploration. Although there is scope in helping hiring managers, there are several possible improvements that need to be made to increase its usability.
Some of the aspects for future work were:
1. Extending the application to recruiting in other domains
2. Exploring ways to help users better trust Watson and the system
3. Incorporating recruiters background for a personalized interview experience, and,
4. Possibly extend this application and test a fully-automated interviewing system.